Finding out if a candidate is a great fit for your team can be incredibly straining. Besides being great at what they do (hard skills), there are tons of other personality traits that they need to have to succeed in their role.
Primarily, these are cognitive abilities – critical thinking, problem-solving skills, learning aptitude, and others.
Today, we’ll tell you everything you need to know about cognitive ability testing for employment.
TL;DR – Key takeaways
Cognitive ability tests measure a person’s logical thinking, deductive reasoning, problem-solving, verbal and spatial reasoning, and other abstract thinking skills.
A cognitive ability assessment can help with forecasting job performance, and they’re easy to use and set up.
However, a cognitive ability assessment can have an adverse impact and may not be ideal for certain types of roles.
There are six main types of common cognitive ability tests: verbal reasoning, numerical reasoning, spatial ability, logical reasoning, learning agility, and perceptual speed and accuracy.
In the future of work, a stronger cognitive ability will become a must to work with AI and machines. Assessing cognitive ability can help you future-proof your workforce.
The more complex the job, the more important cognitive abilities are for performing it well.
The difference between IQ tests and cognitive ability assessments is that the former is a test of general intelligence, while the latter tests specific cognitive ability.
You can assess cognitive ability alongside many job-specific technical and soft skills using the Toggl Hire skills assessment platform. Check out our Test Library or sign up to try it for free!
What is a cognitive ability test?
A cognitive ability test is a test that measures the mental performance of a person.
Cognitive ability tests predict the candidate’s ability for logical thinking, problem-solving, spatial reasoning, verbal reasoning, and others.
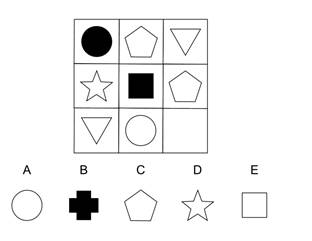
A cognitive ability test or cognitive assessment test aims to show you, as the employer, if a candidate has the cognitive ability to perform well in a job.
As opposed to more practical hard skills tests, many cognitive ability assessments and tests are more abstract in nature.
Some cognitive tests are more specialized (e.g. numerical reasoning, spatial reasoning), while others are more general.
Why use cognitive ability tests during the hiring process?
You may be wondering if it’s worth adding another layer to your hiring process. Or perhaps, whether starting your assessment journey with a cognitive ability test is a good idea.
Here are some pros and cons.
Pros and cons of using cognitive ability tests
Here are some major benefits of using a cognitive ability test during the hiring process:
they are great predictors of job performance
they can be applied to a wide range of jobs
they are easy to set up (with hiring tools like Toggl Hire)
they are easy to complete for candidates
they are relatively cheap when done the right way
However, there are some downsides to bear in mind as well. Here are some reasons why you should not use a cognitive ability test while hiring.
you may face adverse impact, as some cognitive ability tests are better suited for certain population groups
can be limited in their use case, and it’s not ideal for leadership roles that are more complex in nature
In general, cognitive ability tests are an incredible way to predict job performance. Whether used in isolation or combined with other hard skills tests, they’re a reliable way to determine whether a candidate is a good fit for the job and the company.
6 Types of cognitive ability tests and what they assess
There are different types of cognitive ability tests. Rather than going blindly, you should choose the test type that best reflects your ideal candidate’s skills and personality traits.
Verbal reasoning
If you’ve ever done an English test, there’s a good chance you’ve done a verbal reasoning test.
These are language comprehension tests where candidates are given a piece of text to read. After that, they get a range of questions in different formats, such as true/false questions and multiple-choice questions.

The aim of these reading comprehension tests is to determine how well test takers understand concepts expressed through language, draw conclusions from limited information, and how they follow instructions.
Moreover, you can learn much more than just a candidate’s reading comprehension skills. For example, you can tell how well they discern important from unimportant information, process it and apply logic to solve problems.
Numerical reasoning
As the name suggests, numerical reasoning tests aim to determine how well a candidate handles numbers in everyday work situations.
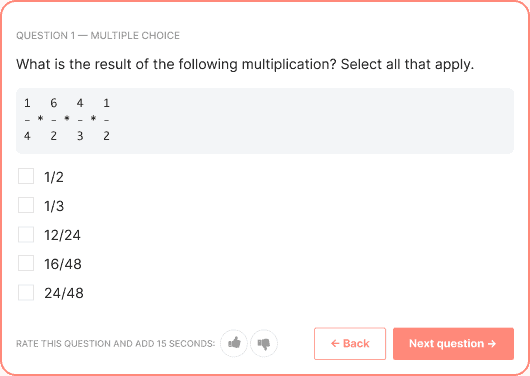
Typical tasks in cognitive ability tests for numerical reasoning include number sequences, percentage calculations, ratio calculations, drawing accurate conclusions from tables, and others.
In the most common scenario, job candidates are given a situation (a graph, table, equation, or something else) and are asked to provide an answer in the form of a number.
These are different levels of math skills, and it’s worth testing for numerical reasoning if you’re hiring for a role that revolves around numbers, such as finance.
Including this type of test in the interview process can save you plenty of headaches in the future.
Spatial ability
If a role requires qualified candidates to visualize objects in space (especially 3D), a spatial ability test will uncover whether they are good at this type of abstract thinking.
Using this type of test is a great starting point for better hiring decisions for roles such as designers and architects.
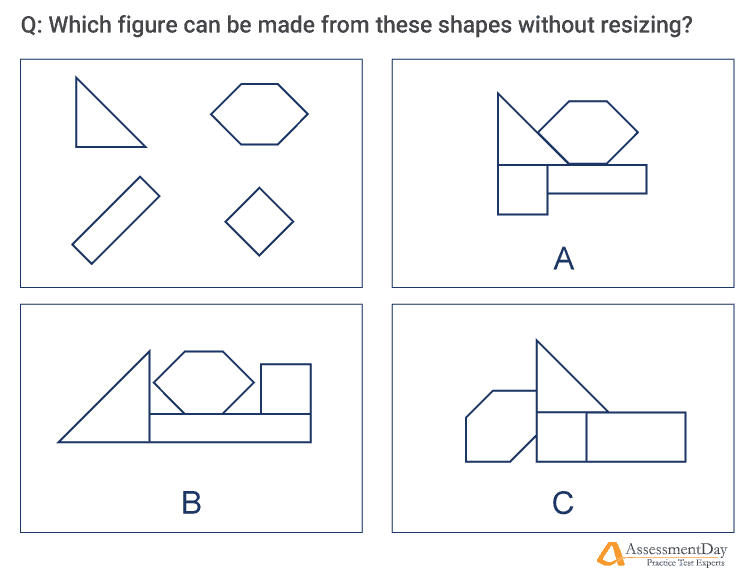
In a typical spatial ability test, candidates are given 3D objects. You then ask the candidates to view the object from a different angle (mentally) and ask them to determine what that angle would look like. Alternatively, you ask candidates to tear apart the object and choose the right components.
As abstract as it may sound, this type of cognitive ability testing can greatly predict job success.
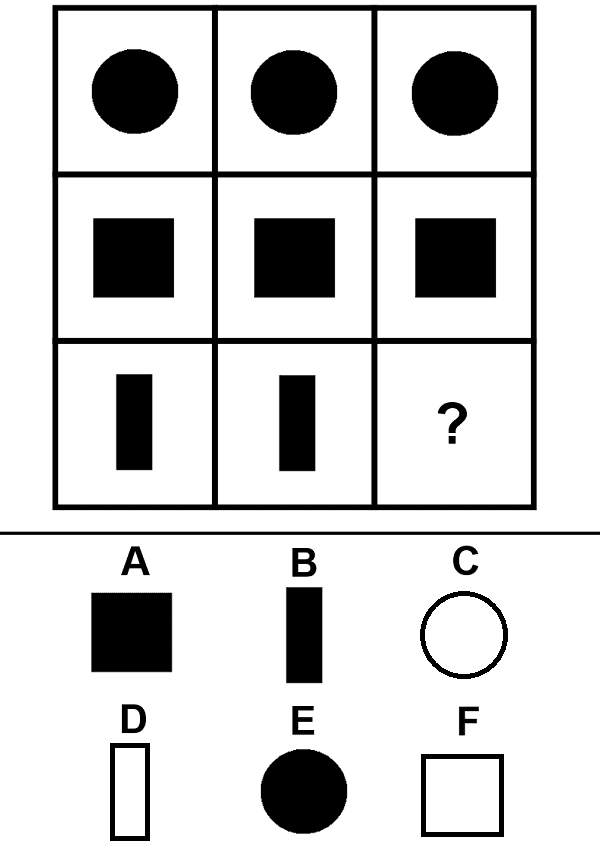
Logical reasoning
A logical reasoning cognitive test shows candidates’ problem-solving skills.
Typically, candidates in this cognitive test are given sequences of objects or numbers and asked to continue the sequence with the most logical item in the line.
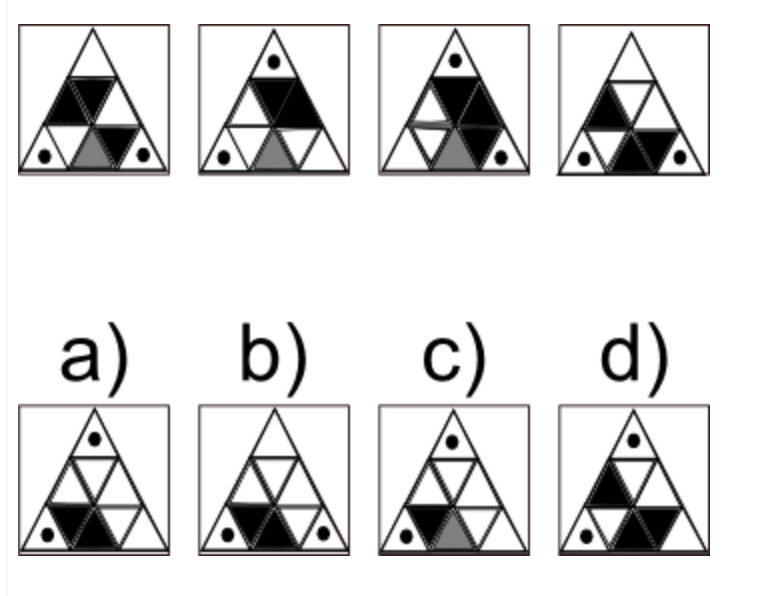
A logical reasoning test shows you the candidate’s ability to think in abstract terms and tests their general intelligence and strategic thinking.
You can use them for any type of job, but they are best suited for roles where candidates need strong problem-solving abilities and critical thinking skills.
Learning agility
This type of cognitive ability test is not focused on job performance.
Instead, it tests the candidate’s cognitive ability to learn on the job. In other words, how quickly they can soak up the information from a fast-paced job and learn new skills.
If you’re hiring for a role with a lot of growth potential or just looking for a self-starter, these cognitive ability tests are a valuable addition to your recruitment process.
Perceptual speed and accuracy
If you’ve ever played a game of Memory Blocks, you’ll know what this is about.
This type of cognitive ability testing is all about giving candidates a body of information in a short time frame and asking them to take action.
In short, it’s about testing candidates’ short-term memory. Just like in a game of Memory Blocks, candidates view a sequence of objects or numbers for a short time and are then asked what they saw and memorized.
The more they can remember, the better their perceptual speed and accuracy and, of course, test scores.
This cognitive aptitude test tells you whether the candidate has the mental skills to solve problems quickly and on their feet.
Examples of how cognitive abilities apply in a workplace
If you’re not reading the news, the future of work is all about AI.
With computers doing much of the heavy lifting in the workplace, cognitive skills are going to become increasingly important.
As research by McKinsey states, there will be less need for manual and basic cognitive skills in the years and decades to come. On the other hand, the future of the workplace will require in-depth cognitive ability, tech skills, and social and emotional skills.
But what about the present?
Let’s say that you’ve used one of these cognitive ability assessments, and a candidate scored really well (or really poorly). How do you interpret the results of your cognitive ability testing?
Here are some cognitive ability testing tips and examples:
Strong verbal reasoning
A candidate is great at understanding different types of information, making their own conclusions, following instructions, and determining what type of information is important.
Strong numerical reasoning
A candidate can quickly make critical decisions regarding numbers, be it the profitability of a marketing campaign or a decision whether you can afford to hire a new team member with your existing budget.
Strong spatial ability
A candidate has a feel for what a design would look like before even lifting a finger in their favorite design app. With this cognitive ability, they can make more intuitive, better decisions about design and space.
Strong logical reasoning
This candidate can analyze a situation from different angles and develop the best, most objective solution to a problem. They ask questions and accept very few things as facts.
Strong learning agility
These candidates have no problems dealing with new situations and problems and can think on their feet. Thanks to this cognitive ability, they find new ways to solve problems and love acquiring new skills.
Strong perceptual speed and accuracy
If you need a candidate who can make critical decisions in a flash, these are your people. They can analyze and summarize information and make quick decisions based on reasoning rather than gut feeling.
Interpreting results about A candidate’s cognitive abilities
On a more general level, all of these cognitive abilities help us develop cognitive skills, such as attention, adaptability, agile and critical thinking, problem-solving, and prioritization.
In the modern workplace, where an AI can do the lion’s share of the work, these cognitive skills are becoming critical for job performance.
As we teach more apps and machines to do the tedious bits in the workplace, humans need to develop stronger mental and critical thinking skills to be able to tell those machines (and other people) what to do and how.
Human intelligence will become a differentiating factor; luckily, a good pre-employment test can help you find stand-out candidates with the right cognitive skills.
Does science back cognitive ability assessments?
So far, the idea of cognitive ability tests sounds good. But what does science say about using cognitive ability tests?
According to the US Office of Personnel Management, cognitive ability assessments are valid when it comes to predicting job performance for a large variety of roles. In fact, the more complex the role, the better these tests can predict how well someone will perform or how successful their training will be.
According to the same institution, cognitive ability assessments will show large differences in data, such as race and ethnicity, compared to other types of tests.
Combining cognitive ability testing with other forms of pre-employment testing related to previous job experiences, such as structured interviews and homework assignments, is best to avoid adverse impact.
If the adverse impact is a huge concern, never rely solely on cognitive ability assessments for hiring.
Perhaps most importantly, the American Psychological Association states that cognitive ability affects how quickly someone can acquire and use new information. Moreover, the more complex the job, the more important should these cognitive assessments be.
What’s the difference between a cognitive ability test and an IQ test?
In general, the two types of tests are fairly similar. Their main aim is to assess candidates’ ability to solve problems and understand different types of concepts. However, they differ in their purpose.
A cognitive ability test is designed to help gauge how well a person tackles a specific type of problem or situation.
An IQ (intelligence quotient) test is a general test of someone’s general mental ability.
In short, an IQ test is much broader in scope and is far less useful in the recruitment process as it can’t tell you much about a candidate’s ability or potential job success.
Evidence-based hiring produces better hires
Cognitive ability tests are just one way to ensure candidates put their money where their mouth is.
With Toggl Hire as your hiring tool, you can go one step further than cognitive ability testing. Check out our extensive library of tests to find hard skills tests for various roles, industries, and use cases. Cognitive ability assessments are just one part of our pool of hiring tests.
Stop relying on your gut feeling when it comes to the most important decisions for your company’s future. Sign up for Toggl Hire and start hiring smarter today.
Juste loves investigating through writing. A copywriter by trade, she spent the last ten years in startups, telling stories and building marketing teams. She works at Toggl Hire and writes about how businesses can recruit really great people.