When was the last time you took an IQ test?
The IQ test is a classic measure of cognitive reasoning. However, it’s not as popular as it used to be for two main reasons.
First, because it cannot fully capture the complexity of human intelligence, and second, because it’s been shown that various factors, like cultural bias or socioeconomic background, can influence results.
Especially when using tests to evaluate candidates, it’s important to be fair, objective, and inclusive. But ultimately, when looking for candidates with strong cognitive skills, are you really looking for the next Stephen Hawking?
Most of the time, it’s about finding someone who has the right mix of cognitive skills to perform well in their role.
In this post, we’ll explore the concept of cognitive reasoning and its importance in the hiring process.
TL;DR – Key Takeaways
- Cognitive reasoning is the brain’s ability to use logic, creativity, and knowledge to understand and solve problems.
- These cognitive reasoning skills are valuable in the workplace as they enhance problem-solving, decision-making, and communication.
- Examples of cognitive abilities at work include customer support managers using linguistic skills and reasoning, financial controllers using perception and problem-solving, and software engineers using critical thinking and pattern recognition.
- You can assess cognitive reasoning in candidates with intelligence tests, cognitive ability tests, psychometric tests, and more.
- Toggl Hire is a hiring tool that can help assess cognitive reasoning in candidates, providing access to a library of tests for various roles, industries, and use cases.
What is cognitive reasoning?
Cognitive reasoning is our brain’s extraordinary ability to use logic, creativity, and knowledge to understand the world around us. We use cognitive reasoning to combine and process our memories, thoughts, and knowledge to solve every and any problem.
It’s all about mental ability, or intelligence, and is crucial in various aspects of daily life, education, work, and play. For example, when faced with a maths problem, our brains start analysing the numbers to calculate the answer. Or when we don’t know how to do something, we use our brains to try to figure it out!
In both cases, speed matters. Because the faster you are at solving problems, the more problems you can solve. But cognitive reasoning goes beyond solving puzzles and maths problems. It also plays a crucial role in decision-making. When faced with multiple options, our brain employs cognitive reasoning to carefully consider the pros and cons and guide us towards the best choice.

Why is cognitive reasoning important in the workplace?
Cognitive reasoning acts as the foundation for a high-functioning team. It equips team members with the ability to interpret data quickly, actively participate in meetings, and solve problems on the spot.
It’s essentially an umbrella term for various skills that fall under cognitive reasoning or ability, such as:
- Problem-solving – Using critical thinking and applying logical reasoning, like inductive reasoning, to identify and resolve complex problems.
- Decision-making – Ability to take all relevant information into consideration, weigh up the pros and cons, and assess the potential outcomes in order to make good, informed decisions.
- Learning and adaptation – The skill of learning and adaptation helps people thrive in changing work environments and continuously evolve in their professions.
- Communication and collaboration – Clear expression of thought, understanding of others’ perspectives, and the ability to work with others.
- Innovation and creativity – Creative thinking empowers individuals to generate unique ideas, overcome challenges, and find innovative solutions.
All of these aspects of cognitive reasoning assist us in completing a wide array of different jobs to the best of our ability.

3 Examples of cognitive skills at work
Cognitive skills are essential for almost every job. To better understand their importance, let’s look at 3 examples of cognitive reasoning at work.
#1 – Customer Support Manager
The goal of a Customer Support Manager is to satisfy the customer and solve his problem quickly. Imagine a scenario where a customer is having trouble with a product or service. The customer is frustrated and angry, and the customer support manager needs to be able to quickly understand the problem to resolve it This requires:
- Attention – The ability to focus on specific information while filtering out distractions.
- Language and Linguistics – The ability to understand and use language effectively, including vocabulary, grammar, syntax, etc.
- Logical Reasoning – The ability to think logically, make deductions, and draw conclusions based on available information.
- Analytical reasoning – The ability to identify and define problems, analyze the situation, generate potential solutions, and select the best course of action.

#2 – Financial Controller
A financial controller plays a critical role in reviewing a company’s financial statements, diligently searching for potential problems such as fraud or critical errors. They are also responsible for making recommendations to improve the company’s financial performance, ensuring that it remains financially stable. This requires:
- Perception – The ability to interpret and make sense of sensory information, such as recognizing patterns and trends in complex financial data.
- Attention – The capacity to focus on specific information while filtering out distractions, allowing for thorough analysis and decision-making.
- Working Memory – The skill to acquire, retain, and recall information accurately, especially related to financial data, ensuring data accuracy and informed decision-making. This will include a general knowledge of the business and its expenses.
- Deductive Reasoning – The aptitude to identify issues, analyze complex financial situations, generate potential solutions, and select the best course of action to optimize financial performance.
- Numerical Reasoning – The capacity to understand and manipulate numerical information.
Need to hire a finance expert? Grab our ready-made assessment template to evaluate all cognitive and job-specific skills required in this role.

#3 – Software Engineer
The role of a software engineer involves designing new features for software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications and collaborating with a team to bring these ideas to life.
To excel in this role, a software engineer must possess a range of cognitive reasoning skills, including:
- Critical Thinking – The ability to think clearly and rationally, approaching problems from different angles to find innovative solutions.
- Methodical Thought Process – Identifying and solving complex coding challenges and outstanding processing skills.
- Abstract Reasoning – Thinking in terms of abstract concepts and applying them to real-world scenarios, allowing for the creation of efficient and scalable software solutions.
- Pattern Recognition – Identifying patterns in data to improve efficiency and effectiveness, enabling the engineer to optimize algorithms and processes.
- Decision-Making – Making informed decisions to complete the task based on available information, considering factors such as feasibility, scalability, and user experience.
Now that we’ve shown you a few examples of cognitive skills in different roles, the question is: how do you test for them?
10 ways to assess cognitive reasoning in your hiring process
There is no single, perfect test to measure cognitive functions in candidates. Human intelligence is far too complex to be captured by a test result. But many different types of cognitive reasoning tests, and test combinations, can be used to effectively assess and compare candidates for specific roles.
As we saw in the 3 examples above, different roles require different cognitive skills and proficiencies. It’s not only the cognitive skill but also the level of skills that matters. That’s why testing for specific skills is more effective than testing for “general intelligence”.
Let’s take a look at the top 10 cognitive reasoning tests, what they assess, and when to use them.
1. Raven’s Progressive Matrices
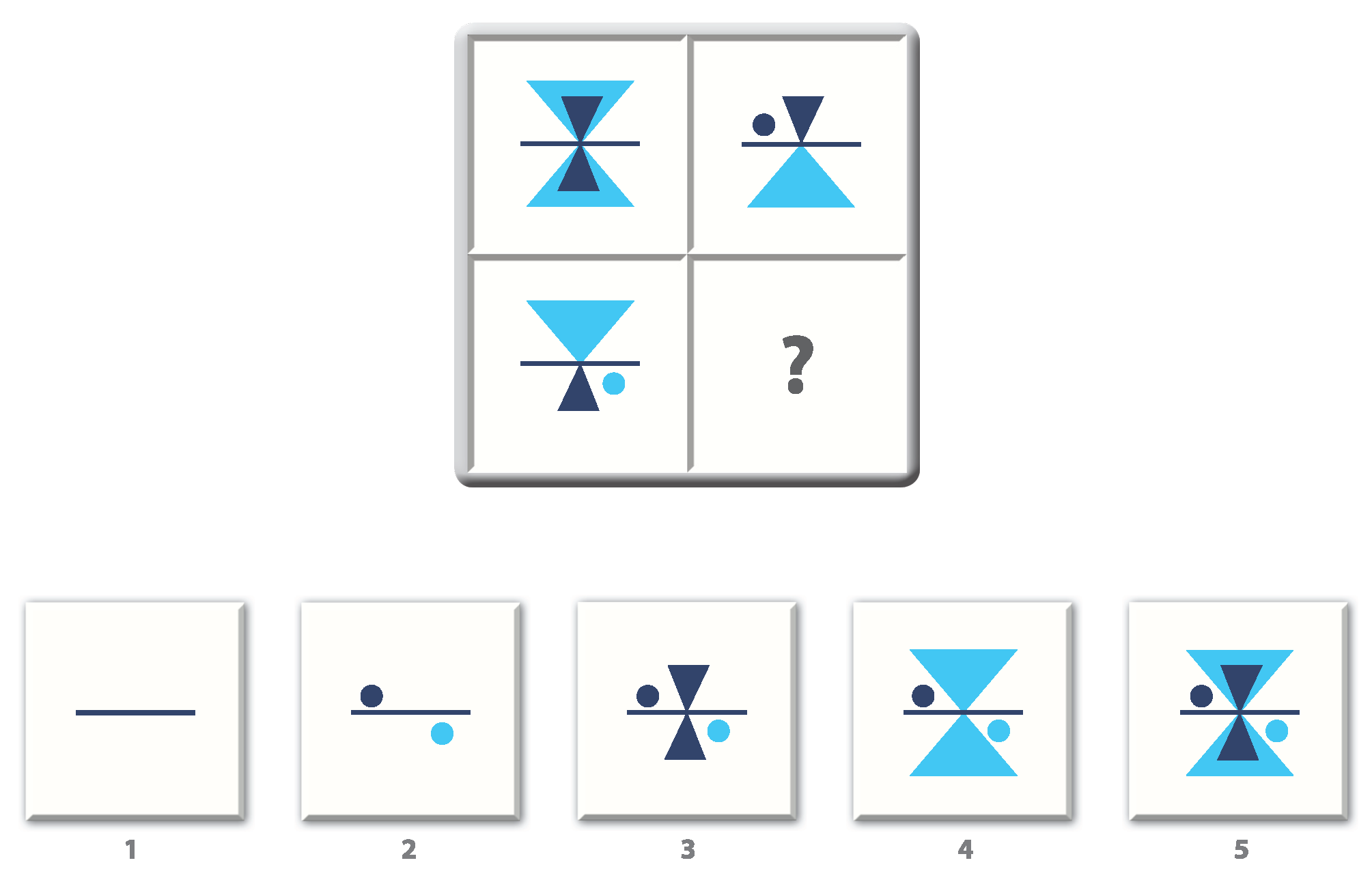
When it comes to cognitive reasoning assessments, Raven’s Progressive Matrices is a popular choice. It’s a non-verbal test that taps into a candidate’s abstract reasoning skills by challenging them to identify patterns and relationships from visual information.
When to use it: This test works best during theinitial screening stages of the hiring process, giving you valuable insights into a candidate’s problem-solving and critical-thinking capabilities.
2. Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal
The Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal is a great tool to understand a candidate’s critical thinking skills. This assessment presents candidates with scenarios and statements requiring careful analysis and drawing conclusions.
When to use it: It’s most effective when used in the later stages of the hiring process, especially when evaluating a shortlist of candidates.
3. Wonderlic Cognitive Ability Test
The Wonderlic Cognitive Ability Test is one of the most versatile cognitive reasoning tests, originally designed for employee selection. It evaluates candidates’ general cognitive skills by measuring their mathematical reasoning, verbal ability, and logical thinking. It’s particularly useful for identifying individuals with strong cognitive skills, indicating their potential to adapt and learn in different job roles.
When to use it: Incorporating this test into the early stages of your hiring process allows you to gauge a candidate’s overall cognitive abilities.

4. Situational Judgment Tests
These provide a realistic simulation of work situations, enabling you to assess a candidate’s ability to adapt, learn, and make effective decisions and gain valuable insights into their problem-solving skills and their suitability for handling complex situations.
When to use it: Using SJTs in the later stages of your hiring process allows you to identify candidates who demonstrate strong learning agility, adaptability, and the potential for growth within your organization.
5. McQuaig Mental Agility Test
You can use the McQuaig Mental Agility Test (MMAT) to assess a candidate’s mental agility, including their quick thinking, problem-solving, and adaptability. It measures cognitive flexibility and the ability to handle complex challenges.
When to use it: Employers can administer this test during the early to mid-stage hiring process to identify candidates with strong mental agility, which is valuable in roles that require quick decision-making and cognitive function.
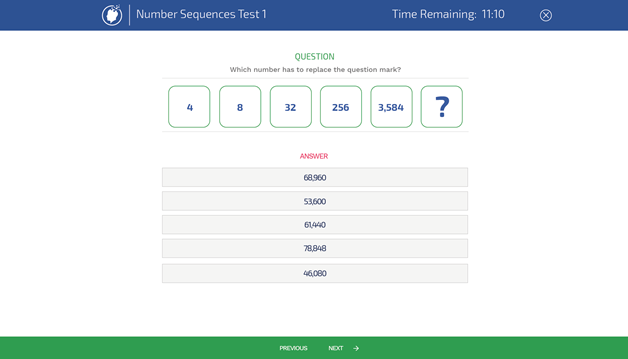
6. Thomas International General Intelligence Assessment
This comprehensive test evaluates a candidate’s general cognitive abilities, including numerical, verbal, and logical reasoning skills, providing an overview of their intellectual capabilities.
When to use it: This assessment is best used in the early stages of the hiring process to gauge a candidate’s overall cognitive capacity and potential for learning and problem-solving.
7. Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory
The Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory (HBRI) is a cognitive assessment that measures a candidate’s ability to solve problems in a business context. It evaluates critical thinking and decision-making skills within real-world work scenarios.
When to use it: This assessment is most effective when assessing candidates for business-related roles in the later stages of the hiring process.
8. Predictive Index Learning Indicator
You should use the Predictive Index Learning Indicator (PLI) to measure reasoning abilities, problem-solving skills, and ability to grasp new concepts.
When to use it: Employers can administer this test during the early stages of the hiring process to identify candidates with a strong aptitude for learning and adapting to new challenges.

9. Revelian Cognitive Ability Tests
The Revelian Cognitive Ability Tests (RCAT) evaluate a candidate’s cognitive skills, including numerical, verbal, and abstract reasoning.
When to use it: The RCAT can be employed at various stages of the hiring process, depending on the specific cognitive skills needed for the role.
10. Criteria Cognitive Aptitude Test
The CCAT is an assessment measuring cognitive reasoning skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving and logical reasoning. Additionally, the test evaluates the aptitude for learning and adapting rapidly.
When to use it: The CCAT is effective during the initial screening stages of the hiring process to identify candidates with strong cognitive aptitude, which is crucial for various roles requiring analytical and problem-solving abilities.
📚 Top 5 Cognitive Ability Assessment Tools
Hire candidates with excellent cognitive reasoning skills with Toggl Hire
Toggl Hire is a hiring tool that can help you assess the cognitive abilities of candidates. With Toggl Hire, you can access our extensive library of tests to find skills tests for various roles, industries, and use cases. Cognitive reasoning assessments are just one part of our pool of hiring tests.
By using Toggl Hire, you can get a complete picture of a candidate’s cognitive reasoning skills. This information can help you make better hiring decisions and hire candidates more likely to succeed in your organization.
Juste loves investigating through writing. A copywriter by trade, she spent the last ten years in startups, telling stories and building marketing teams. She works at Toggl Hire and writes about how businesses can recruit really great people.






